Paper Computer Network Bahasa Inggris II BSI
COMPUTER NETWORK
Lecturer
: Palupi, S.S, M.Pd.
Compiled
By :
Class
12.2A.21
1.
Herlina 12144316
2.
Uswatun Khasanah 12145143
3.
Elfiatun Nurul Hidayah 12145199
4.
Fanny Fatmawati 12145216
5.
Riyan Latifahul Hasanah 12145229
6.
Rizka Nurul Khasanah 12145230
7.
Lili Nurhartanti 12145335
Manajemen
Informatika
Bina
Sarana Informatika Purwokerto
2015
PREFACE
First at all, give thanks for
God’s love and grace for us.
Thanks to God for helping us
and give us chance to finish this assignment timely. And we would like to say
thank you to Mrs. Palupi S.S, M.Pd. as
the lecturer that always teaches us and give much knowledge about how to
practice English well.
This paper was made to obtain
the value of the task subjects in English. We realized this assignment is not
perfect. But we hope it can be useful for us. Critics and suggestion is needed
here to make this assignment be better.
Hopefully we as a student in
“AMIK BSI Purwokerto” can work more professional by using English as the second
language whatever we done. Thank you.
Compiler
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PREFACE i
TABLE OF CONTENTS ii
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION
A. Issue Background 1
B. Problem
Identification 1
C. Limitation of the
Problems 1
D. Problem Formulation 1
CHAPTER II : DISCUSSION
A. Definition of Computer Network 2
B. Type of Computer
Network 2
C. Characteristics Different Type of Network 4
D. Devices for Computer Network 7
CHAPTER III : FINAL
A.
Knot 9
B. Advice 9
BIBLIOGRAPHY 10
INTRODUCTION
A.
Issue Background
Technological
developments have made many remarkable progress. Many things from life sector
that has used the existence of the technology itself. Presence has a
considerable impact on the lives of human beings in various aspects and
dimensions. Likewise with the communication technology is hardware equipment in
the organizational structure that contains social value that enables
individuals to collect, process and exchange information (in Rogers, 1986)
In the development of
technology to the network, where each device can interact with another devices
and another computers, from the local network to the global network, called the
Internet. In this paper the author will try to explain the various computer
networks.
B. Identification Problems
(Background)
In
accordance with the title of this paper “Computer Network” , the problem can be
identified as follows :
a) What is the meaning of
computer network?
b) What the various
types of computer networks?
c) What are the
characteristics of various types of network?
d) What kind of devices used in computer network
C. Limitation of the
Problem
To
clarify the scope of the discussion , the issues addressed are limited to the
issue :
a) Understanding computer
network
b) Understanding various
type of computer network
c) Understanding the
characteristics different type of network
d) Understanding devices for computer network
D. Problem Formulation .
Based
on the background and the issue of limitation, the issues discussed can
beformulated as follows :
a) What kinds of uses of
computer network topology?
b) What sense of
topology, protocol and architecture?
c) What devices is used
to create a computer network?
CHAPTER II
DISCUSSION
A. Definition
of Computer Network
The Meanings of Computer Network :
·
A computer network is a group of
interconnected computers.
·
A
computer network is a collection of computing devices
that are connected in various ways in order to communicate and share resources.
·
A network is a collection of
computers connected to each other. The network allows computers to communicate
with each other and share resources and information.
Usually, the
connections between computers in a network are made using physical wires or
cables. However,
some connections are wireless,
using radio waves or infrared signals. The benefit of a computer network
are : Sharing
hardware resources easily and Sharing information easily.
The Advanced
Research Projects Agency (ARPA) designed "Advanced Research Projects
Agency Network“ (ARPANET) for the United States Department of Defense. It was
the first computer network in the world in late 1960's and early 1970's.
B.
Type of Computer
Network
1.
Local-area
Networks (LANs)
·
The computers are geographically
close together (that is in the same building).
·
A network that connects a relatively
small number of machines in a relatively close geographical area.
2.
Wide-area
Networks (WANs)
·
The computers are farther apart and
are connected by telephone lines or radio waves.
·
A network that connects two or more
local-area networks over a potentially large geographic distance
Local-area Networks connected across a distance to create a Wide-area Network
3.
Campus-area Networks
(CANs)
The computers
are within a limited geographic are a, such as a campus or military base.
4. Metropolitan-area
Networks
(MANs)
A data
network designed for a town or city.
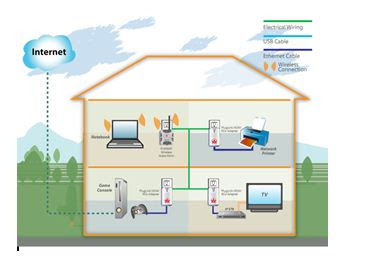
5. Home-area Networks
(HANs)
A network
contained within a user's home that connects a person's digital devices.
C. Characteristics Different Type of Network
The
following characteristics are used to categorize different types of networks:
1.
Topology
· The
geometric arrangement of a computer system.
·
The network topology defines the way
in which computers, printers, and other devices are connected. A network
topology describes the layout of the wire and devices as well as the paths used
by data transmissions.
· Common
topologies include a bus, star, and ring.
A.
Bus
Topology
All nodes
are connected to a single communication line that carries messages in both
directions. Commonly
referred to as a linear bus, all the devices on a bus topology are connected by
one single cable.
B. Ring Topology
A
configuration that connects all nodes in a closed loop on which messages travel
in one direction.
A frame travels around the ring, stopping at each node. If a node wants
to transmit data, it adds the data as well as the destination address to the
frame. The frame then continues around the ring until it finds the destination
node, which takes the data out of the frame.
• Single ring
– All the devices on the network share a single cable
• Dual ring –
The dual ring topology allows data to be sent in both directions.
C.
Star Topology
A
configuration that centers around one node to which all others are connected
and through which all messages are sent. The star topology is the most
commonly used architecture in Ethernet LANs. When
installed, the star topology resembles spokes in a bicycle wheel. Larger
networks use the extended star topology also called tree topology. When used
with network devices that filter frames or packets, like bridges, switches, and
routers, this topology significantly reduces the traffic on the wires by
sending packets only to the wires of the destination host.
D.
Mesh Topology
The mesh topology connects all devices (nodes) to each other for
redundancy and fault tolerance. It is used in WANs to interconnect LANs and for
mission critical networks like those used by banks and financial institutions.
Implementing the mesh topology is expensive and difficult.
2. Protocol
The protocol
defines a common set of rules and signals that computers on the network use to
communicate.
Two of the most popular protocols for LANs is called Ethernet and the
IBM token-ring network
3. Architecture
Networks can
be broadly classified as using either a peer-to-peer or client/server
architecture. Computers on a network are sometimes called nodes. Computers and
devices that allocate resources for a network are called servers.
D.
Devices for Computer Network
There are
many kinds of devices to create a computer network. For a basic computer
network we would need :
- Network Interface Cards
A network
card, network adapter or NIC (network interface card) is a piece of computer
hardware designed to allow computers to communicate over a computer network.
NIC can be identified easily. It has a special port called RJ-45. RJ means
Registered Jack. And also a led to indicate a data is being transferred.
- Repeaters
A repeater
is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it at a higher
power level, or to the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can
cover longer distances without degradation.
- Hub
A hub
contains multiple ports. When a packet arrives at one port, it is copied to all
the ports of the
hub for transmission. When the packets are copied, the destination address in
the frame does not change to a broadcast address. Below is a picture of 5-port
ethernet hub.
- Router
A device that
forwards data packets between computer networks, creating an overlay
internetwork. A router is connected to two or more data lines from different
networks. When a data packet comes in one of the lines, the router reads the
address information in the packet to determine its ultimate destination. Then,
using information in its routing table or routing policy, it directs the packet
to the next network on its journey. Routers perform the "traffic
directing" functions on the Internet.
CHAPTER III
CLOSING
CLOSING
A.
Knot
Based on the description of the
discussion “Computer Network” can be concluded that :
1. A network is a collection of computers connected to
each other. The network allows computers to communicate with each other and
share resources and information.
2. Various types of
computer networks are Local-area networks (LANs), Wide-area networks (WANs),
Campus-area networks (CANs), Metropolitan-area networks (MANs) and Home-area
networks (HANs)
3.
Characteristics of various types of networks are Topology, Protocol and Architecture
4. For a basic
computer network we would need Network Interface Cards, Repeaters and Hub
A. Advice
1.
Computer network technology help us in a
variety of activities . Therefore, use them wisely so as not to harm others
2.
Expand our knowledge of computer network
BIBLIOGRAPHY
http://vfu.bg/en/e-Learning/Computer-Networks--Network.ppt
= = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = =
Baca juga materi Semester 2 UBSI lainnya:
- Latihan Soal UAS Pengantar Organisasi Komputer BSI Semester 2
- Perancangan Basis Data - Membuat ERD Kasus Puskesmas
- Rangkuman Pengantar Organisasi Komputer Pertemuan 14
- Klasifikasi Komputer berdasarkan Perkembangan dan Data yang Diolah
- Paper Computer Network Bahasa Inggris II BSI
- Contoh Makalah Pembuatan Program Mata Kuliah Struktur Data BSI
- Soal Review UAS Perancangan Basis Data BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UAS Pengantar Organisasi Komputer BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Struktur Data BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UAS Struktur Data BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UAS Dasar Manajemen dan Bisnis BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Pendidikan Agama Islam BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Essay Struktur Data BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS (2) Pengantar Organisasi Komputer BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Dasar Manajemen dan Bisnis BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Pengantar Organisasi Komputer BSI Semester 2
= = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = =
Baca juga materi Semester 2 UBSI lainnya:
- Latihan Soal UAS Pengantar Organisasi Komputer BSI Semester 2
- Perancangan Basis Data - Membuat ERD Kasus Puskesmas
- Rangkuman Pengantar Organisasi Komputer Pertemuan 14
- Klasifikasi Komputer berdasarkan Perkembangan dan Data yang Diolah
- Paper Computer Network Bahasa Inggris II BSI
- Contoh Makalah Pembuatan Program Mata Kuliah Struktur Data BSI
- Soal Review UAS Perancangan Basis Data BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UAS Pengantar Organisasi Komputer BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Struktur Data BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UAS Struktur Data BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UAS Dasar Manajemen dan Bisnis BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Pendidikan Agama Islam BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Essay Struktur Data BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS (2) Pengantar Organisasi Komputer BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Dasar Manajemen dan Bisnis BSI Semester 2
- Soal Review UTS Pengantar Organisasi Komputer BSI Semester 2

















Komentar
Posting Komentar